Secure File Uploads to Amazon S3 Using Presigned URLs
When building modern web applications, one common challenge is allowing users to upload or download files directly to and from Amazon S3 while maintaining proper security controls. Directly exposing your S3 bucket to the public is a security risk, and routing large files through your application servers wastes resources and increases costs.
This is where presigned URLs combined with a serverless architecture provide an elegant solution.
What Are Presigned URLs?
Presigned URLs are temporary, time-limited URLs that grant access to specific S3 objects without requiring the end user to have AWS credentials. These URLs embed authentication information in the query parameters, allowing anyone with the URL to perform the authorized action (upload or download) until the URL expires.
The beauty of presigned URLs is that they enable direct client-to-S3 communication while you maintain complete control over who can access what and for how long.
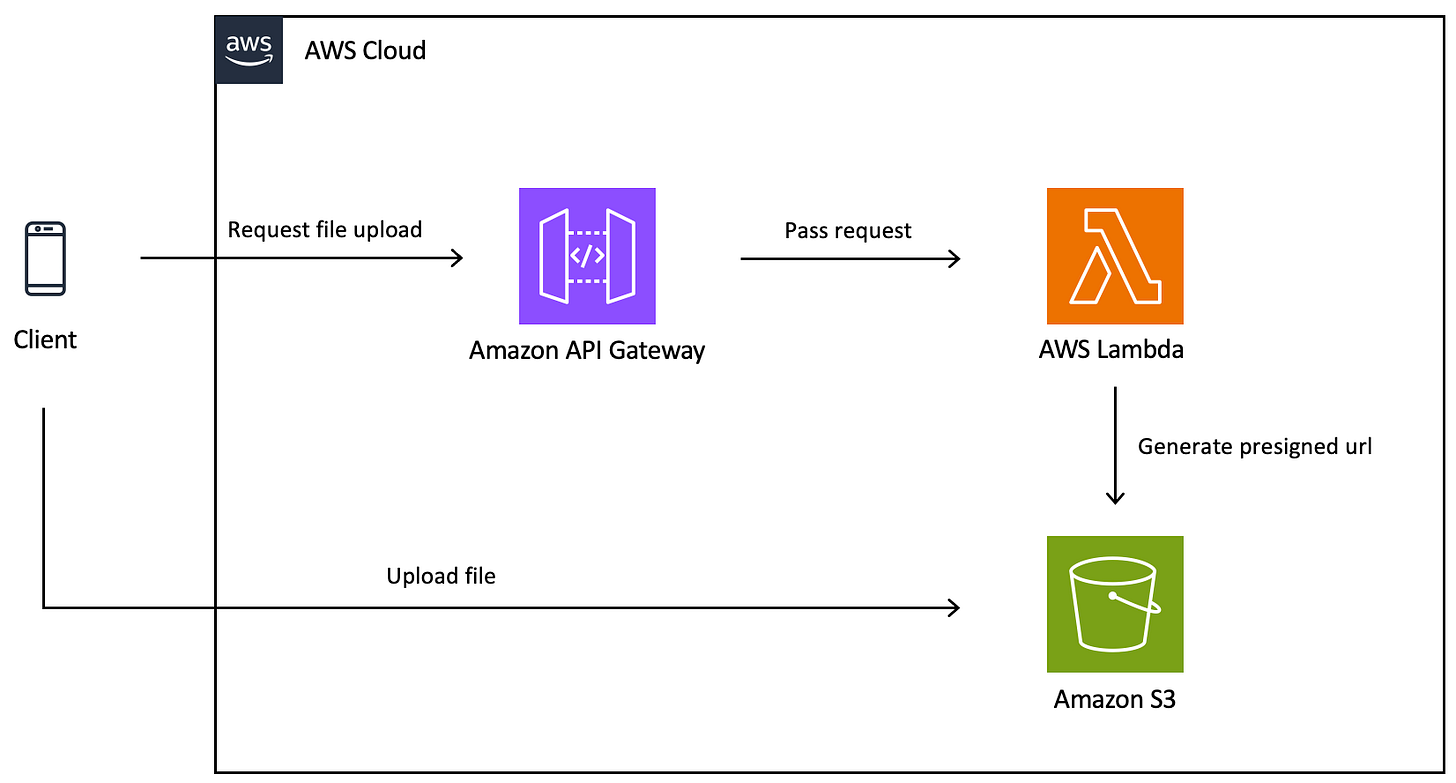
The Serverless Architecture Flow
Components Overview
The solution involves three core AWS services:
API Gateway: Acts as the secure front door for your application
AWS Lambda: Generates the presigned URLs with appropriate permissions
Amazon S3: Stores your files securely
The Upload Flow
Step 1: Client Request The client application makes an authenticated request to your API Gateway endpoint, asking for permission to upload a file. This request typically includes metadata like filename, file type, and size.
Step 2: API Gateway Authentication API Gateway validates the request using your chosen authentication method—this could be AWS Cognito, Lambda authorizers, or IAM authentication. This ensures only legitimate users can request upload permissions.
Step 3: Lambda Processing Once authenticated, API Gateway triggers your Lambda function. The Lambda function:
Validates the request parameters
Checks business logic (file size limits, allowed file types, user quotas)
Generates a unique S3 key/path for the file
Creates a presigned URL for PUT operations with an expiration time (typically 5-15 minutes)
Step 4: Presigned URL Response The Lambda function returns the presigned URL to the client through API Gateway. This URL contains temporary credentials embedded in the query parameters.
Step 5: Direct Upload The client uses the presigned URL to upload the file directly to S3 using a standard HTTP PUT request. This happens completely outside of your API infrastructure—the file never touches your Lambda function or API Gateway.
Step 6: Upload Completion Once the upload completes, your client application can notify your API (through another endpoint) that the upload finished, allowing you to update database records or trigger additional processing.
The Download Flow
The download process follows a similar pattern:
Step 1: Download Request The client requests access to download a specific file through your API Gateway endpoint.
Step 2: Authorization Check API Gateway authenticates the request, and Lambda verifies that the user has permission to access the requested file.
Step 3: Presigned URL Generation Lambda generates a presigned URL for GET operations with an appropriate expiration time.
Step 4: Direct Download The client uses the presigned URL to download the file directly from S3, bypassing your application infrastructure entirely.
Security Benefits
This architecture provides multiple layers of security:
Authentication and Authorization: API Gateway ensures only authenticated users can request presigned URLs, and Lambda can implement fine-grained authorization logic.
Time-Limited Access: Presigned URLs expire after a set time period, minimizing the window for potential abuse.
Private S3 Buckets: Your S3 bucket remains completely private with no public access policies needed.
Audit Trail: API Gateway and Lambda both generate CloudWatch logs, giving you complete visibility into who requested access to what files.
No Credential Exposure: End users never need AWS credentials or direct S3 access.
Best Practices
Keep expiration times short: For uploads, 15 minutes is typically sufficient. For downloads, adjust based on expected file sizes and download speeds.
Validate everything in Lambda: Don’t trust client input. Always validate file types, sizes, and paths on the server side.
Implement rate limiting: Use API Gateway throttling to prevent abuse.
Monitor and alert: Set up CloudWatch alarms for unusual patterns in presigned URL generation.
Consider S3 event notifications: Trigger Lambda functions when uploads complete to scan files, update databases, or start processing workflows.
Cost Efficiency
This architecture is highly cost-effective because:
Large files transfer directly to S3 without consuming Lambda execution time
You only pay for the brief Lambda execution that generates the URL
API Gateway charges only for the initial request, not the data transfer
S3 data transfer is charged at standard rates, which are typically lower than processing costs
Conclusion
Combining presigned URLs with a serverless architecture provides a secure, scalable, and cost-effective solution for managing file uploads and downloads. By leveraging API Gateway for authentication, Lambda for business logic, and presigned URLs for direct S3 access, you create a system that’s both secure and performant.
This pattern is production-ready and scales automatically with your application’s needs, making it an excellent choice for modern cloud-native applications on AWS.