5 Proven Strategies to Reduce Cold Starts in AWS Lambda
In the world of serverless computing, AWS Lambda is a game-changer, allowing developers to run code without managing servers. However, one challenge that developers often face is the infamous cold start. This delay occurs when a Lambda function is invoked after being idle, leading to increased latency. In this article, we’ll explore five strategies to optimize cold starts for your Lambda functions, ensuring your applications remain responsive and efficient.
Understanding Cold Starts
Before we dive into the strategies, let’s first understand what a cold start is.
Cold starts in AWS Lambda occur when a function is invoked for the first time after being deployed or after a period of inactivity. During a cold start, the Lambda service needs to set up a new execution environment, which includes provisioning resources, initializing the runtime, and loading your code and dependencies. This process can introduce significant latency, impacting the performance of your application.
To ensure your Lambda functions perform efficiently, it's crucial to minimize cold start times. Here are five strategies to help you achieve this:
1. Optimizing Memory
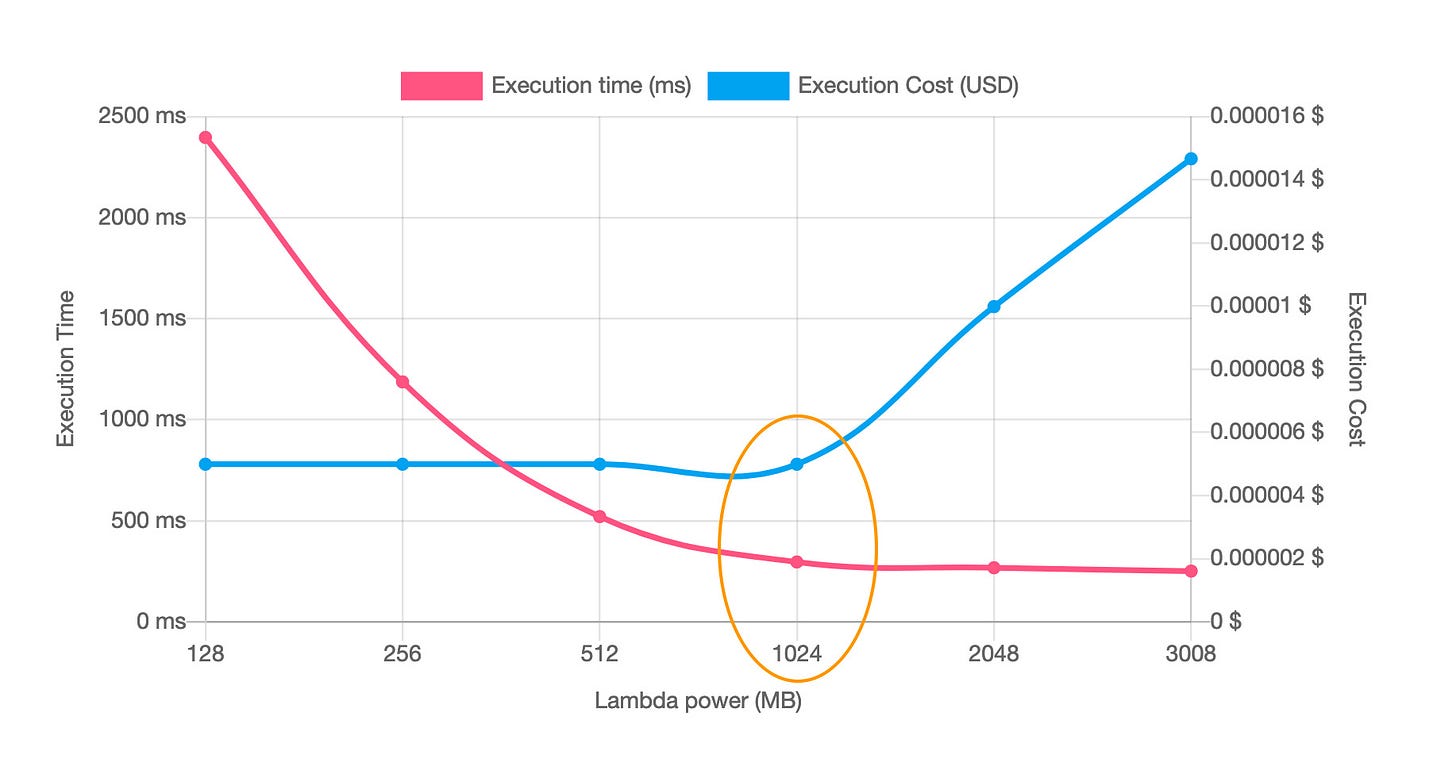
Memory allocation directly affects the performance of your Lambda functions. Allocating more memory can provide more CPU power and network bandwidth, which can reduce cold start times. However, it's essential to find the right balance to avoid over-provisioning, which can lead to increased costs.
Lambda Power Tuning is a useful tool for finding the optimal memory configuration. It automatically tests different memory settings and identifies the configuration that offers the best performance-to-cost ratio. By running Lambda Power Tuning, you can ensure that your functions are configured with just the right amount of memory to minimize cold starts without overspending.
2. Use Graviton 2
AWS Lambda supports functions running on ARM-based Graviton2 processors, which offer better price-performance compared to x86 architectures. Graviton2 processors can provide up to 34% better price-performance.
By migrating your Lambda functions to Graviton2, you can take advantage of these performance improvements, leading to faster cold starts and reduced latency. Ensure that your dependencies and runtimes are compatible with ARM architecture before making the switch.
3. Move Code Outside the Handler Method
One effective way to reduce cold start times is to move initialization code outside the handler method. Code executed outside the handler runs only once when the function is initialized, rather than on every invocation.
For example, instead of initializing libraries or setting up connections within the handler, perform these tasks during the function's startup phase. This approach ensures that the overhead of initialization is amortized across multiple invocations, leading to faster subsequent executions.
4. Minimize Dependencies
The number and size of dependencies in your Lambda function can significantly impact cold start times. Each dependency adds to the deployment package size, which increases the time required to download and extract the package during initialization.
Review your function’s dependencies and remove any that are not essential. Additionally, consider using smaller, more lightweight libraries where possible. This reduction in package size can lead to faster cold starts and improved overall performance.
5. Use SnapStart
Lambda SnapStart is a feature that significantly reduces cold start times by taking a snapshot of your function’s initialized runtime and state. When a function is invoked after a period of inactivity, Lambda restores the function from the snapshot rather than initializing it from scratch.
Enabling SnapStart can lead to substantial reductions in cold start latency, making your functions more responsive. This feature is particularly beneficial for Java-based Lambda functions, as it addresses the long initialization times associated with the Java Virtual Machine (JVM).
Conclusion
Cold starts can be a significant performance bottleneck for AWS Lambda functions. By implementing these five strategies—optimizing memory with Lambda Power Tuning, using Graviton2 processors, moving code outside the handler method, minimizing dependencies, and leveraging SnapStart—you can substantially reduce cold start times and enhance the performance of your serverless applications.



Great breakdown! curious, which one of these gave you the biggest cold start drop?